MG Pilot safety features: how do they work?
From alerting you to potential collision hazards, to clever systems that help you to maintain traction and stability. Your safety is our main concern. That’s why we created MG Pilot with clever assistance technologies, all designed to help keep you, your family and other road users protected.
MG Pilot includes a range of ADAS that warn the driver of potential danger and intervene if necessary. All with the aim of making your driving experience easier, more enjoyable and above all, safer. MG Pilot covers 12 driver assistance systems, almost all of which are standard on all MG models.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) monitors the road ahead. As long as the road ahead is clear, ACC maintains the speed set by the driver. If the system spots a slower vehicle within its detection range, it gently reduces speed by releasing the accelerator or actively engaging the brakes. If the vehicle ahead speeds up or changes lanes, ACC automatically accelerates back to the driver’s desired speed.
Intelligent High Beam Control (IHC)
When the headlight high beam is set to the AUTO position, the system automatically switches to low beam when it detects a vehicle ahead. This enables drivers to maximise the use of high beam, making night-time driving safer, while reducing the risk of dazzling on-coming traffic.
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
At speeds below 20 km/h, the vehicle will automatically apply its brakes to avoid a collision with other road users. At speeds above 20 km/h, AEB will reduce the likelihood or severity of an accident.
Front Collision Warning (FCW)
This technology continuously monitors the distance between the driver’s vehicle and the vehicle in front. It also keeps an eye on the driving speed. If the distance between the two vehicles (suddenly) becomes too narrow, taking into account the driven speed, FCW will alert the driver of an impending collision.
Traffic Jam Assistance (TJA)
When Adaptive Cruise Control is turned on, Traffic Jam Assist continuously monitors the speed of the vehicle in the front. If the system detects dense traffic or a traffic jam at speeds below 60 km/h, the driver can activate TJA. The driver’s vehicle will automatically follow the vehicle in front, controlling its acceleration, braking and steering within the same lane.
Lane Departure Warning (LDW)
Lane Departure Warning uses a camera to detect lane markings on the road ahead and monitors the vehicle’s position in its lane. When the function detects the vehicle is about to unintentionally move out of its lane, it warns the driver by means of a visual, audible and steering wheel vibration.
Lane Keep Assistance (LKA)
Lane Keep Assist works much the same as Lane Departure Warning, but goes a step further. When the function detects the vehicle is about to unintentionally move out of its lane, it doesn’t only warns the driver, but also adjust and control the steering to keep the vehicle within its lane.
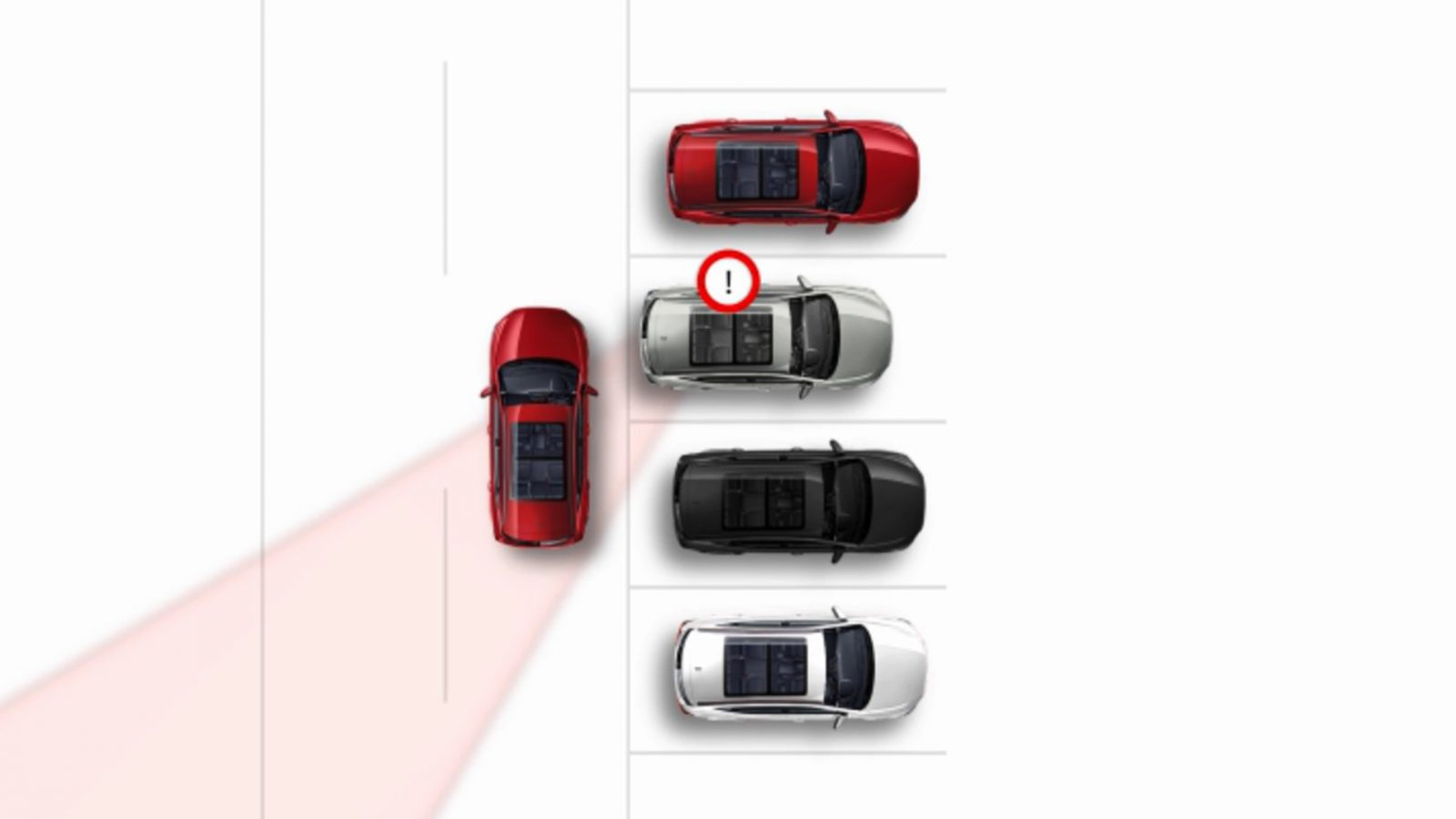
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM)
This safety system monitors the blind spots on the right and left rear. If a vehicle is in the blind spot and not visible in the door mirror, the Blind Spot Monitoring system alerts the driver. By displaying a visual signal on the door mirror on the side where the vehicle is detected.
Lane Change Warning (LCW)
If the driver doesn’t notice the signal from the Blind Sport Monitoring and wants to change lanes while a vehicle is in the blind spot, the Lane Change Warning system provides an additional visual, audible and tactile warning to (help) avoid a collision.
Rear Traffic Alert (RTA)
Rear Traffic Alert warns the driver of vehicles approaching from either side when reversing. This is especially useful when reversing out of a parking space and you cannot see if cross traffic is approaching.
Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR)
Traffic Sign Recognition recognizes various road signs thanks to a special forward-facing camera. It then displays the main road sign on the instrument display to provide additional driver awareness.
Speed Assistance System (SAS)
This system is an extension of TSR. It actively detects speed limit signs and alert the driver of the current speed limit with a symbol on the driver’s instrument cluster, reducing the risk of exceeding the speed limit.